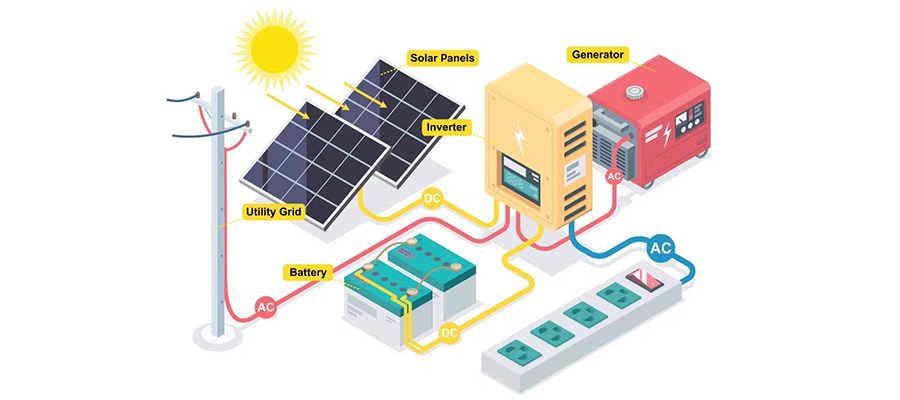
Overview of Solar Inverters
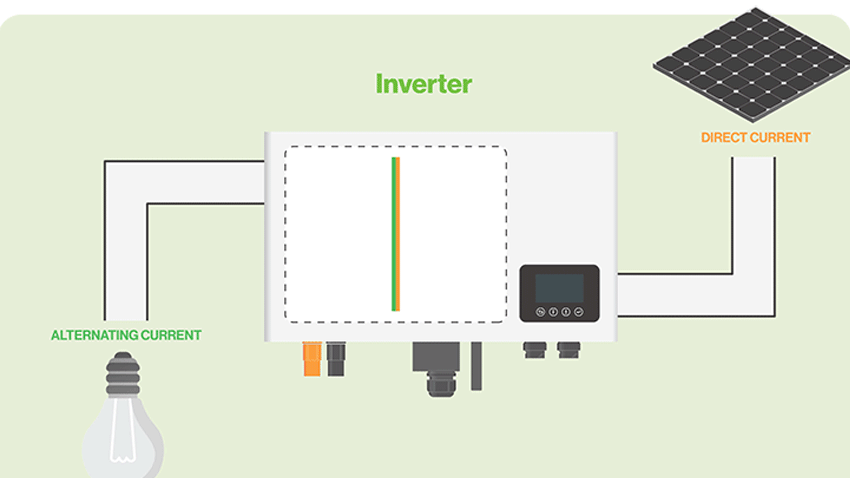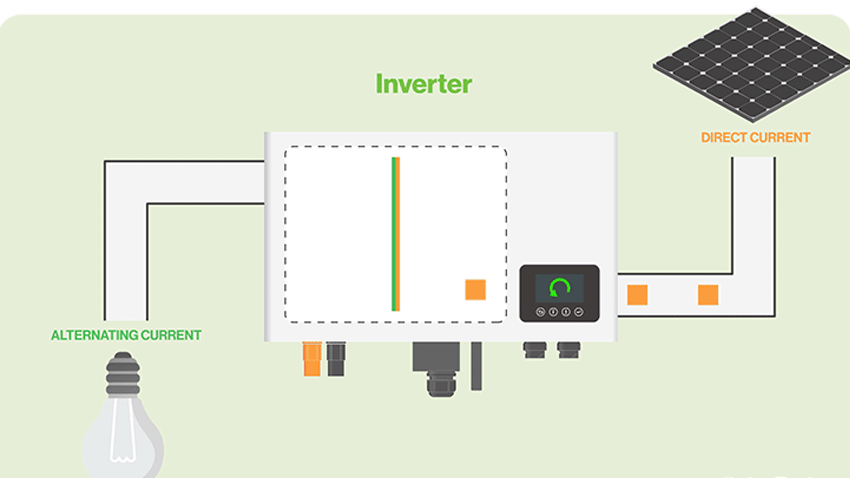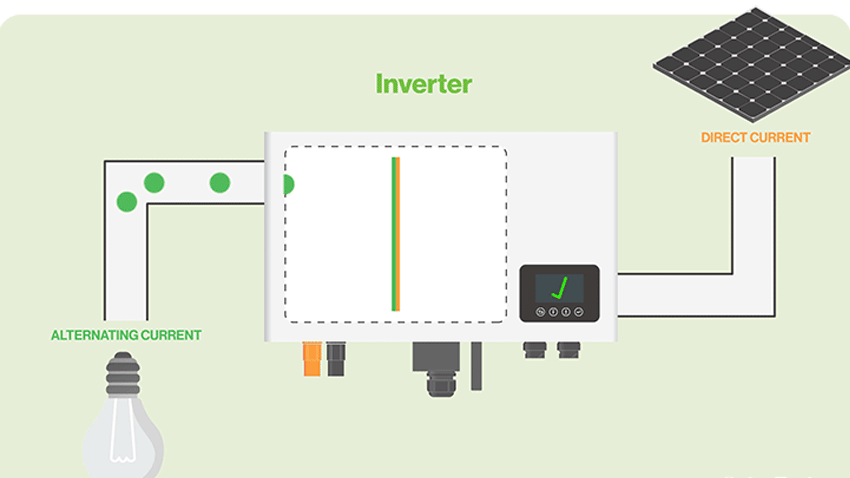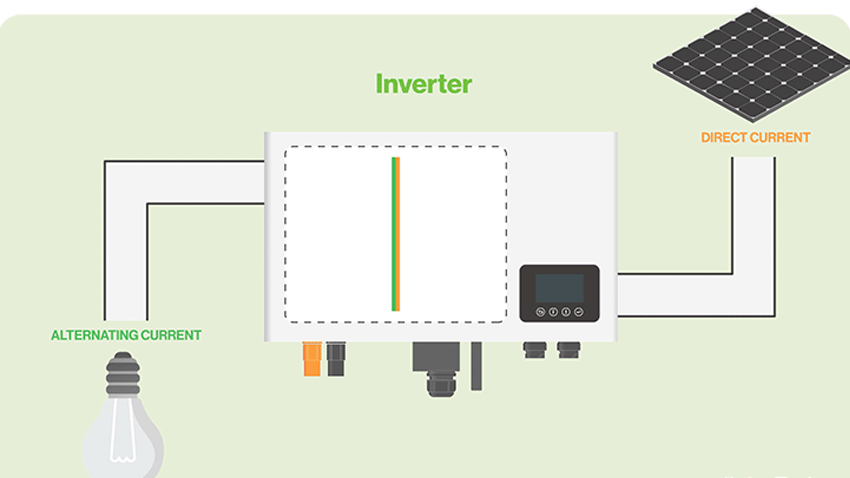
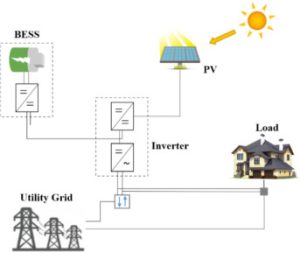
A solar inverter is a component in a solar panel installation that’s designed to convert direct current (DC) electricity into alternating current (AC) electricity. Power grids, of course, typically distribute AC electricity. AC electricity lives up to its namesake by alternating its direction. It can change direction, thereby allowing it to travel across longer distances than that of DC electricity. Solar inverters are responsible for converting the DC electricity produced by a solar panel installation into AC electricity.
Whether monocrystalline or polycrystalline, solar panels almost always produce DC electricity by default. Exposure to sunlight causes the electrons within their photovoltaic material to move around and become “excited.” This movement results in the production of DC electricity. To use the solar panel installation’s electricity in a home or building, it must be converted into AC electricity, which is the solar inverter’s job. The solar inverter will perform the DC-to-AC conversion so that the electricity can be used to power devices in a home or building.
How Solar Inverters Work
Most solar inverters look like small boxes. They are installed between a solar panel installation and the home or building that it powers. The DC electricity produced by a solar panel installation will enter the solar inverter where it’s converted into AC electricity. After leaving the solar inverter, the newly converted AC electricity will enter the home or business.
Of course, there are different types of solar inverters. Some of the most common types include battery solar inverters, central solar inverters, micro solar inverters and hybrid solar inverters. Regardless, they all work by taking the DC electricity produced by solar power installation and converting it into AC electricity.
Varieties of Solar Inverters: A Kaleidoscope of Efficiency
Diversity reigns supreme in the domain of solar inverters, with each variant sculpted to address distinct exigencies. Herein lie some of the most prevalent incarnations:
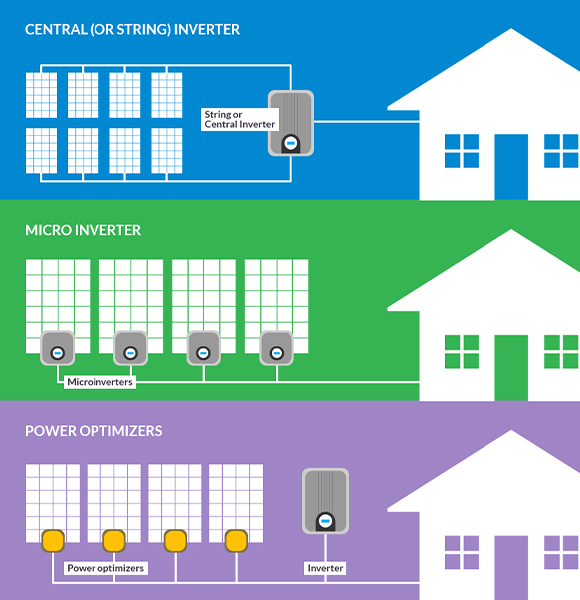
1. String Inverters: The quintessential workhorse of solar energy systems, string inverters, forms the backbone of many installations. These adept devices stand in a sequential constellation, interconnected in strings where multiple solar panels contribute to a collective energy output. While string inverters excel in reliability and cost-effectiveness, they bear susceptibility to the ‘weakest link’ phenomenon – where a single panel’s shading or malfunction dampens the entire string’s efficiency.
2.Microinverters: Conceived as a panacea for the string inverter’s limitations, microinverters exemplify the era of distributed intelligence. Attached to individual solar panels, microinverters grant each panel autonomy, optimizing energy production even in the shadow of impediments like shading or panel disparities. Notably enhancing system performance, microinverters champion real-time monitoring, empowering homeowners to wield granular insight into each panel’s productivity.
3.Power Optimizers: Power optimizers, akin to microinverters, grace panels at an individual level. However, their modus operandi is distinct – optimizing the DC output before channeling it to a central inverter. This hybrid methodology amalgamates the virtues of both centralized and decentralized optimization paradigms, endowing the system with flexibility and efficiency.
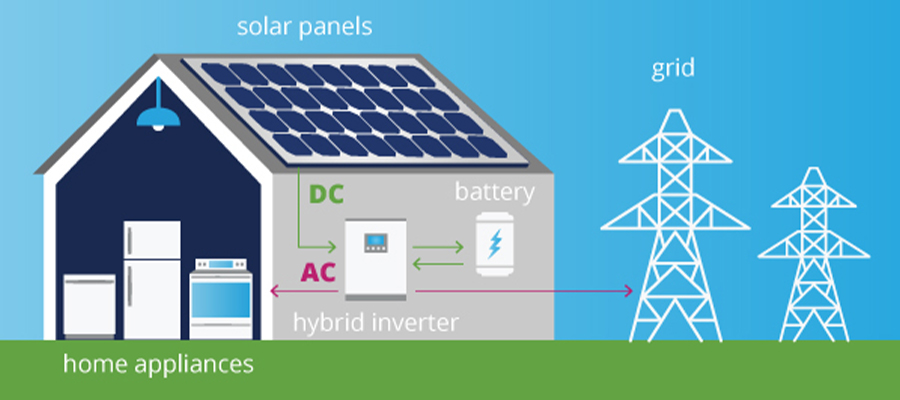
4.Hybrid Inverters: In an era where energy storage forges its path, hybrid inverters emerge as the vanguards of progress. Facilitating the coalescence of solar power and energy storage, these chameleonic entities orchestrate the storage of surplus solar energy within batteries. The result? A harmonious dance between sustainable solar power and energy autonomy, fortifying resilience against grid fluctuations.
Benefits of a Solar Inverter
Maximize Energy Production
Solar inverters keep track of voltage to discover the maximum power that the modules can function. Because it focuses on solar array voltage, you get the cleanest energy possible. A grid tie solar inverter produces maximum energy compared to its low-cost counterparts.
The modified sine wave ensures efficient energy for the most sensitive appliances. This is the voltage the inverter makes over time without damaging the electrical components. Remember, your solar inverter will allow for more power than the maximum AC output for conversion losses.
Monitoring System Output
A solar power inverter generates thousands of watts every day. The inverter offers a way to help you view how much power you’re using. Some allow you to track performance using a mobile app. If the modules are upgraded, the unit will identify the string’s peak.
If things aren’t working as they should, the unit alerts you automatically. Even better, you can use the tracking system to check whether the system is producing the right amount of electricity.
Some systems measure energy production with a charger controller. The data can also be monitored via Wi-Fi, so you can assess the system via mobile.
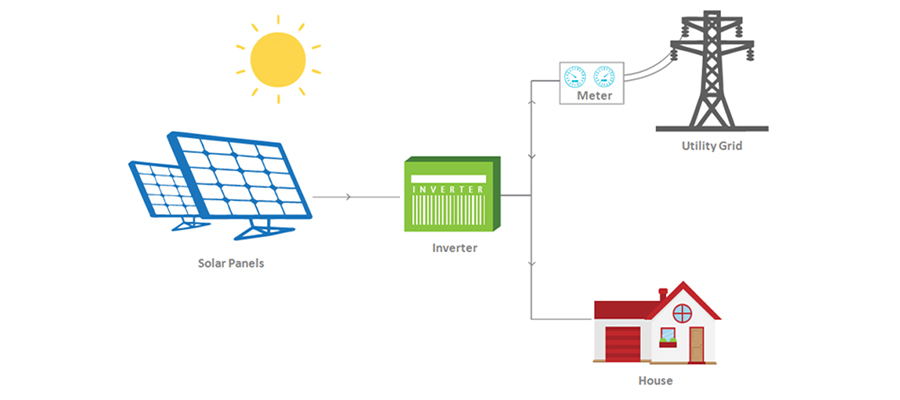
Communicating with the Utility Grid
If there’s a temporary power outage, the solar power inverter ensures electricity is not transmitted to external power lines. New smart inverters have a way of communicating with the grid. They carry out grid-supportive tasks that relate to frequency, communication, voltage, software, and controls.
Any line worker on the grid is protected from injuries. If your home doesn’t require all the energy produced, the surplus can help you generate energy credits. In case of voltage change, a smart inverter can turn into standby mode. If the disturbance persists, the system turns off automatically.
Evolving Solar Inverter Frontiers
The evolution of solar inverter technology is a saga of relentless innovation, aiming to amplify efficiency, dependability, and integration prowess. The intrepid crusaders of research and engineering unravel novel frontiers to enhance solar inverter performance, surmount shading dilemmas, and seamlessly intertwine energy storage. Sundry advancements dot this odyssey, including:
Advanced MPPT Algorithms: Pioneering Maximum Power Point Tracking (MPPT) algorithms, equipped with adaptive capabilities, stand poised to revolutionize energy optimization. By dynamically responding to shifting conditions – be it shading or atmospheric turbulence – these algorithms extract maximal energy from each panel, elevating efficiency to unprecedented heights.
Smart Inverter Intelligence: The rise of smart inverters heralds a new era of interactive technology. Armed with communication prowess, these paragons engage in a nuanced dance with the grid, channeling reactive power support and aligning with demand response programs. The result? Grid stability elevated to an art form.
Blockchain Integration: The marriage of solar inverters and blockchain technology emerges as an enticing prospect, enshrining transparency and traceability within the energy ecosystem. Solar inverters, functioning as data sentinels, immortalize energy production and consumption data on the blockchain, catalyzing efficient peer-to-peer energy trading.
Enhanced Monitoring and Prognostics: The realm of real-time monitoring and diagnostics burgeons with sophistication. The modern solar inverter becomes a repository of insights, endowing homeowners and operators with real-time performance snapshots. This vantage facilitates proactive maintenance and timely issue resolution.
Forging Ahead: Solar Inverters as Architects of a Sustainable Odyssey
Amid the global sprint towards renewable energy ascendancy, solar power unfurls as the crown jewel in the pantheon of sustainability. The solar inverter, with its chameleonic ability to metamorphose sunbeams into usable electricity, constitutes the veritable backbone of this green revolution. As technology forges forward, and as the spheres of research and exploration expand, solar inverters are poised to burgeon in efficiency, metamorphosing into paragons of reliability and integration.
Consequently, as individuals, corporations, and nations awaken to the manifold advantages of solar energy – from curtailing greenhouse gas emissions to eviscerating energy expenditures – the role of solar inverters cannot be overstated. These inconspicuous sentinels stand sentinel over an era of boundless solar potential, illuminating a path towards a radiant, verdant, and sustainable future for generations yet to tread upon this Earth.