When considering the installation of a solar power system, a multitude of decisions awaits, and since this involves an investment in equipment with a long lifespan, making informed choices is crucial. Engaging with a trusted solar installer can provide tailored guidance through these decisions to ensure you obtain the ideal system for your specific situation. Nevertheless, conducting some preliminary research can be beneficial. Therefore, we’re outlining the four distinctions between on-grid and off-grid solar power to assist you in determining which option suits your solar project best.
Understanding Off-Grid Solar System and On-Grid Solar System
An off-grid solar energy system stands independent of the utility grid, relying exclusively on solar and battery-stored energy. Conversely, an on-grid, or grid-tied, solar energy system is intricately connected to the utility grid, influencing critical factors such as electricity access, handling of excess production, responses during grid outages, and the nuances of billing mechanisms.
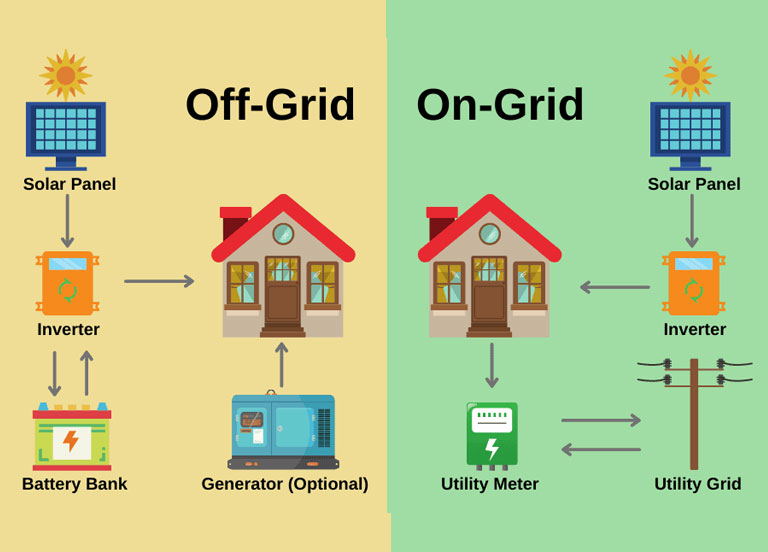
Delving into the Differences Between Off-Grid and On-Grid Solar Energy
- Electricity Access:
– Off-Grid Solar: Hinging entirely on solar and stored battery energy, access is limited during periods of low solar production.
– On-Grid Solar: Promises uninterrupted access, seamlessly drawing from the grid during periods of inadequate solar generation.
- Excess Production Handling:
– Off-Grid Solar: Surplus energy is stored in batteries for later use, ensuring autonomy but necessitating substantial battery investments.
– On-Grid Solar: Excess energy can be seamlessly fed back into the grid, often compensated through mechanisms like net metering, providing a cost-effective storage alternative.
- Grid Outage Response:
– Off-Grid Systems: Exhibit resilience during power outages, continuing to operate independently of the grid for uninterrupted service.
– Grid-Tied Systems: In the absence of battery backup, grid-tied systems lose electricity during grid outages due to safety regulations.
- Billing for Electricity:
– Off-Grid Systems: Traditionally, no electric bills are received, but higher initial costs are incurred due to necessary equipment like batteries.
– On-Grid Systems: Despite solar contributions, minimal charges such as service fees or demand charges may persist on electricity bills.
Hybrid Solar Energy Systems: A Comprehensive Solution
Hybrid systems emerge as a middle ground, combining grid connectivity with battery storage. While these systems command a higher upfront cost due to the integration of batteries, they offer benefits such as uninterrupted power during outages and potential reductions in demand charges, particularly beneficial for businesses seeking a balance between grid reliability and energy autonomy.
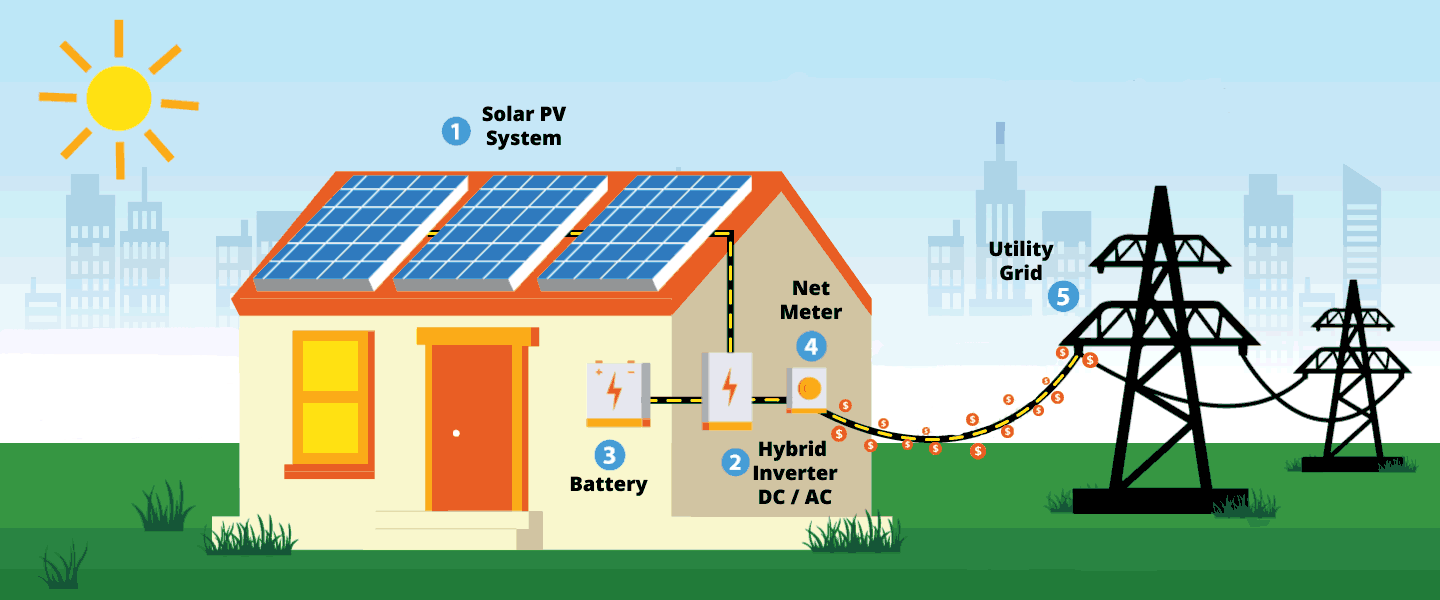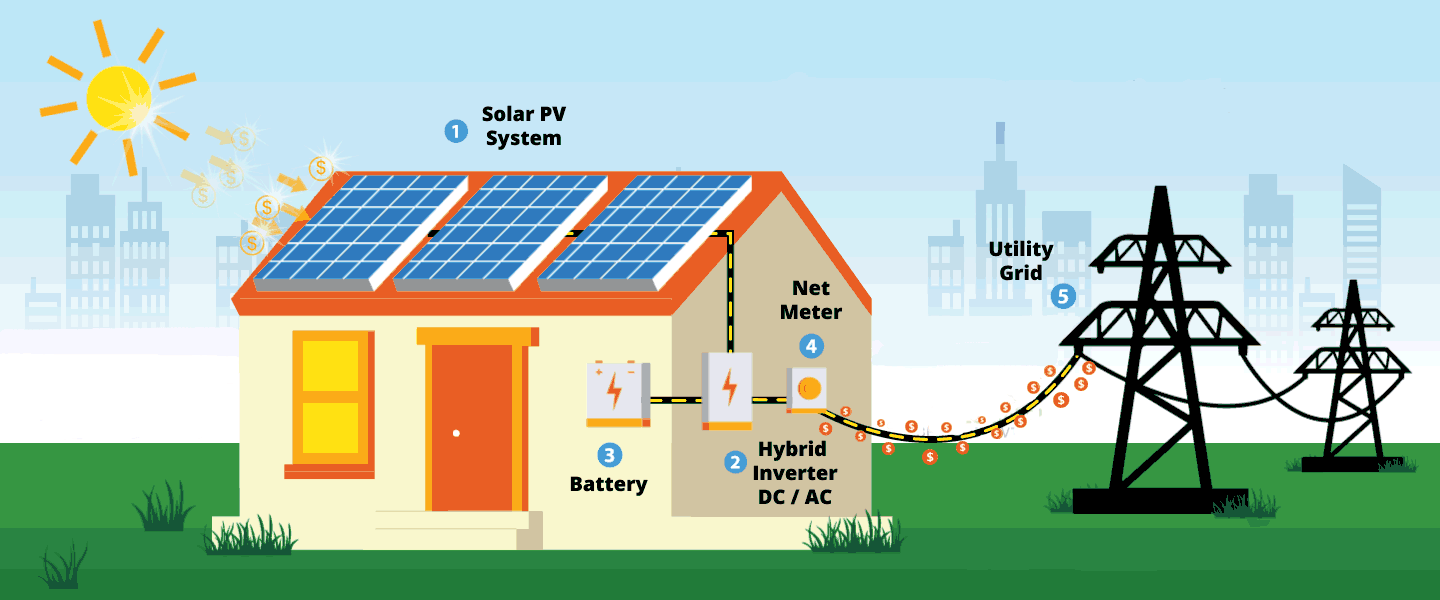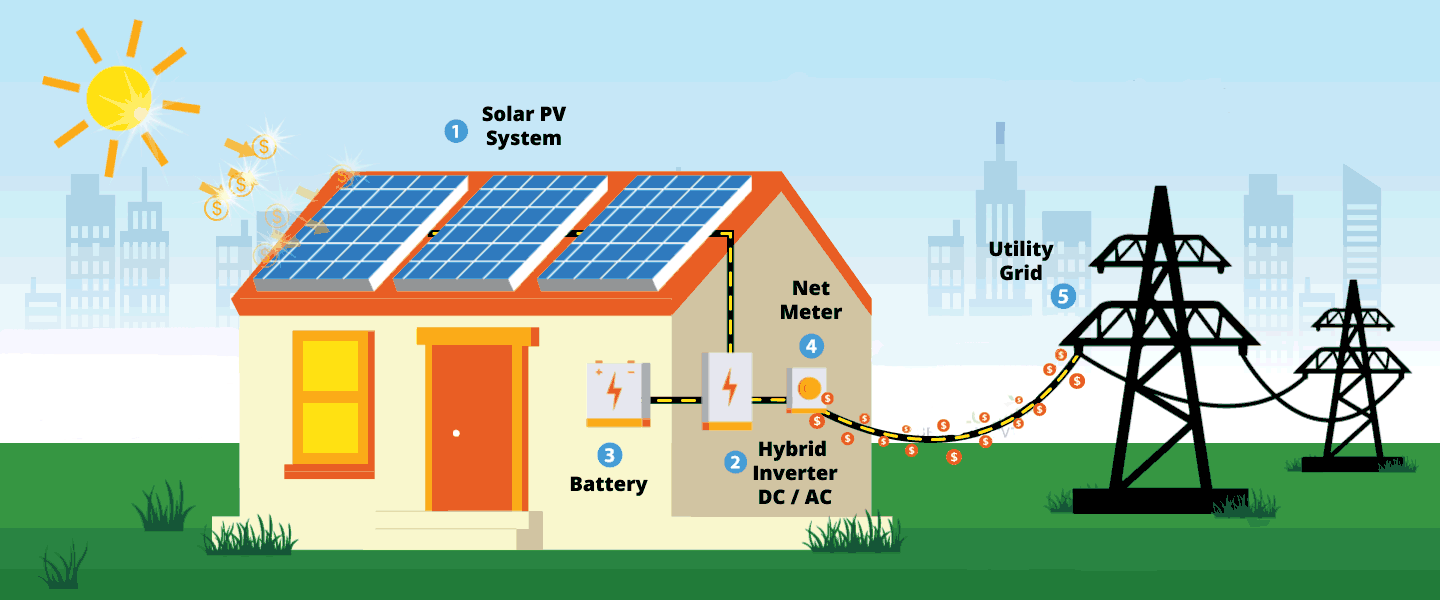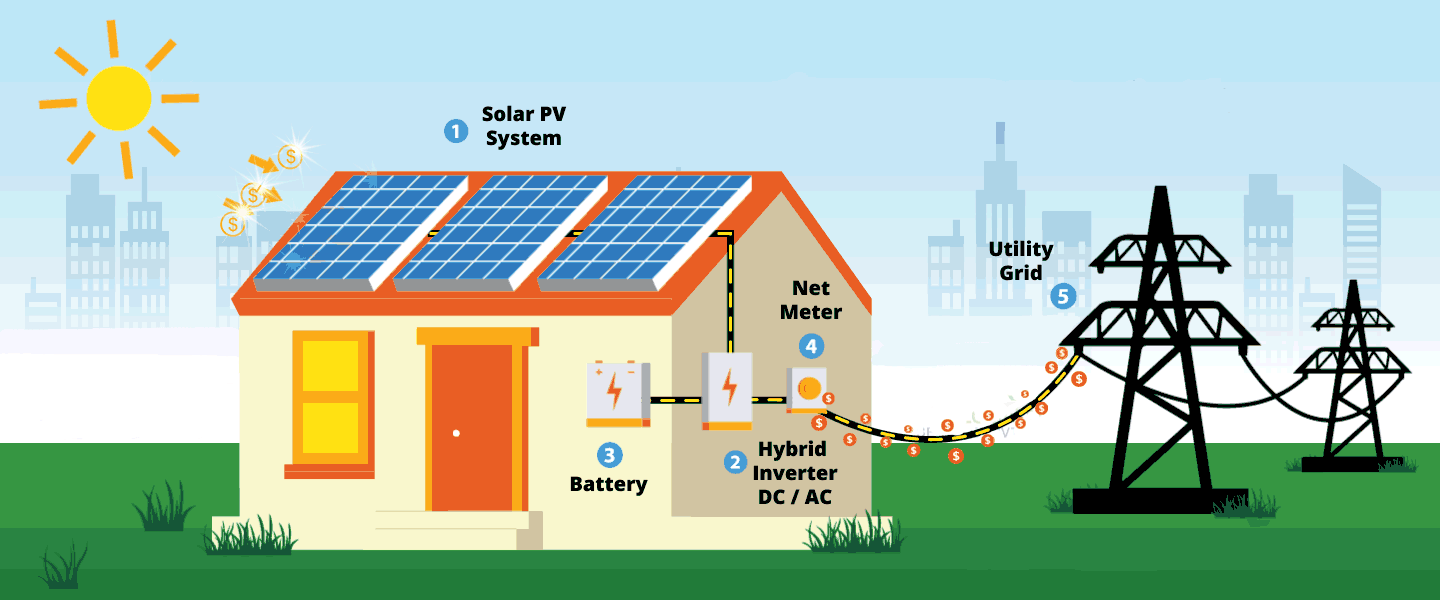
In conclusion, acquiring an in-depth understanding of these distinctions empowers individuals to make well-informed decisions when venturing into solar energy investments. Collaborating with an experienced solar installer further refines this decision-making process, ensuring the selection of a solar system tailored to specific needs and preferences.
Choosing the right power capacity for a solar system involves considering various factors, including your energy consumption, available space for solar panels, budget, and environmental conditions.
Here’s a guide on how to choose the appropriate power capacity for a solar system and what components are typically included in a solar power system:
Choosing Solar System Power Capacity:
- Determine Your Energy Needs:
– Start by understanding your average daily and monthly electricity consumption. This information helps estimate the size of the solar system required to meet your energy needs.
- Consider Available Space:
– Evaluate the available space for installing solar panels. Different panel types have varying efficiency levels, and the amount of sunlight your location receives can impact the system’s overall performance.
- Budget Considerations:
– Establish a budget for your solar project. The cost of solar panels and installation varies, and setting a budget helps narrow down your options and find a system that meets your financial constraints.
- Local Solar Resources:
– Consider the solar irradiance or sunlight availability in your location. Areas with more sunlight can generate more electricity, impacting the required system size.
- Incentives and Rebates:
– Check for available solar incentives, rebates, and tax credits in your area. These can significantly reduce the overall cost of your solar system.
- Future Expansion:
– Consider whether you might need to expand your solar system in the future. If so, choose a system that allows for scalability.
Before designing a solar system, you also need to know the Components of a Solar Power System:
– Photovoltaic (PV) solar panels are the primary components that convert sunlight into electricity. Monocrystalline and polycrystalline panels are common types.
– Converts the direct current (DC) generated by solar panels into alternating current (AC) used by household appliances. Inverters can be string inverters, microinverters, or power optimizers.
- Mounting Structure:
– Provides the support structure for solar panels. The mounting system can be roof-mounted, ground-mounted, or integrated into building materials.
- Solar Racking:
– Holds the solar panels in place and ensures they are securely attached to the mounting structure.
- Battery Storage (Optional):
– Batteries store excess energy generated during the day for use during periods of low sunlight or at night. This is optional but can provide energy independence and backup during power outages.
- Charge Controller (if using batteries):
– Regulates the charge going into the batteries to prevent overcharging and extend battery life.
- Monitoring System:
– Allows you to track the performance of your solar system, monitor energy production, and identify potential issues.
- Electrical Wiring and Disconnects:
– Connects the various components of the system and provides a safe way to shut down the system for maintenance.
- Grid Connection (for Grid-Tied Systems):
– In grid-tied systems, a connection to the utility grid allows for the exchange of excess electricity with the grid and access to power during periods of low solar production.
- Permits and Documentation:
– Obtain the necessary permits and documentation required by local authorities for the installation of a solar power system.
Remember to consult with a professional solar installer to assess your specific needs and ensure a customized solar solution tailored to your requirements and circumstances.
Here are some solar systems with different power for different applications:
* 3kW Solar System : A 3kW solar system presents an optimal solution for smaller-scale power applications. Compact and cost-effective, it caters to the energy needs of small to medium-sized homes with substantial electricity consumption. Tailored for households of two to three individuals, as well as smaller homes with heightened energy demands, the 3kW solar PV system emerges as a reliable and economical choice.
Key application scenarios encompass:
- Household electricity for 2-3 people
- Small farms
- Remote areas
- Emergency standby power
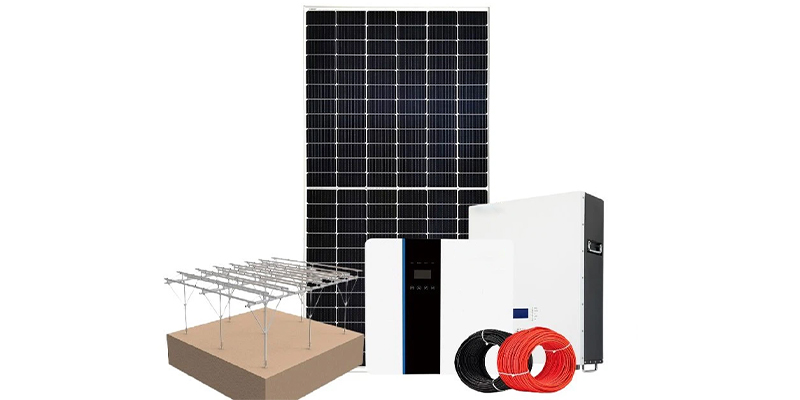

* 5KW Solar System with Lithium-Ion Battery: The 5KW solar system, complemented by a lithium-ion battery, serves as a medium-sized solution suitable for family homes, modest commercial structures, or larger residences with moderate energy consumption. Consisting of 14 solar panels, a 5KW lithium-ion battery, and a CE approved 5KW inverter, this system, installed by certified retailers, addresses the rising costs of electricity bills. It is well-suited for various applications, including:
- Household electricity for 5-8 people
- Small farms, villas
- Remote areas
- Emergency standby power
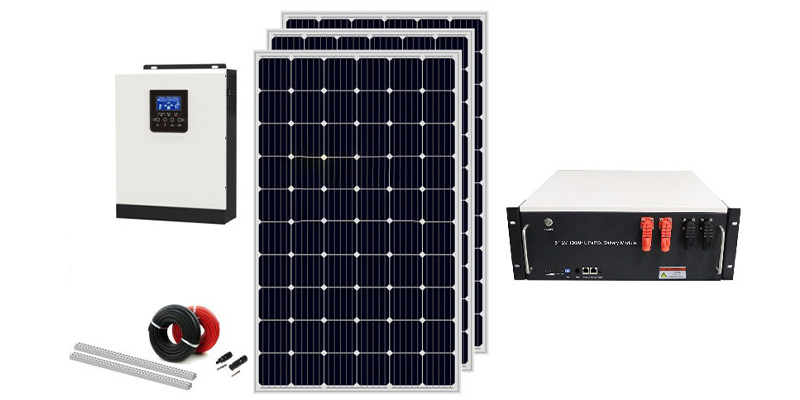

* 8kW Solar System: Tailored for large households with elevated energy needs, the 8kW solar system stands out for its superior power output. Ideal for sizeable residences or minor commercial applications, its popularity is attributed to an advantageous price-to-capacity ratio. This system, generating sufficient electricity to meet daytime household needs, finds resonance in scenarios such as:
- Household electricity for 2-3 people
- Small farms
- Remote areas
- Emergency standby power
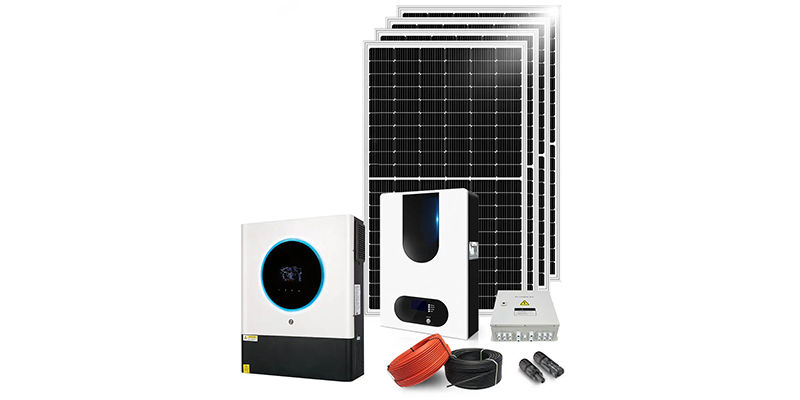

* 10kW Solar System: A 10kW solar system emerges as the ideal choice for large homes, offering clean and dependable electricity. Well-suited for electric car owners or those contemplating such a purchase in the future, this system accommodates both off-grid and on-grid residential energy storage solutions. Tailored for diverse applications, including:
- Household electricity for a country house
- Farms, villas
- Remote areas
- Emergency standby power
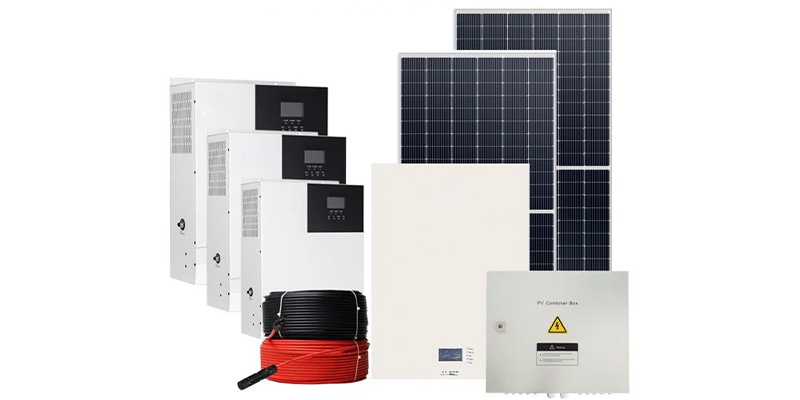

These solar systems cater to a spectrum of energy needs, providing efficient and cost-effective solutions for various residential and commercial scenarios.
To accurately design your ideal solar system and provide you with a quote, you can contact us here for more details and suggestions.
